Quick Sort C Linked List
Quicksort on singly linked list was given as an exercise.
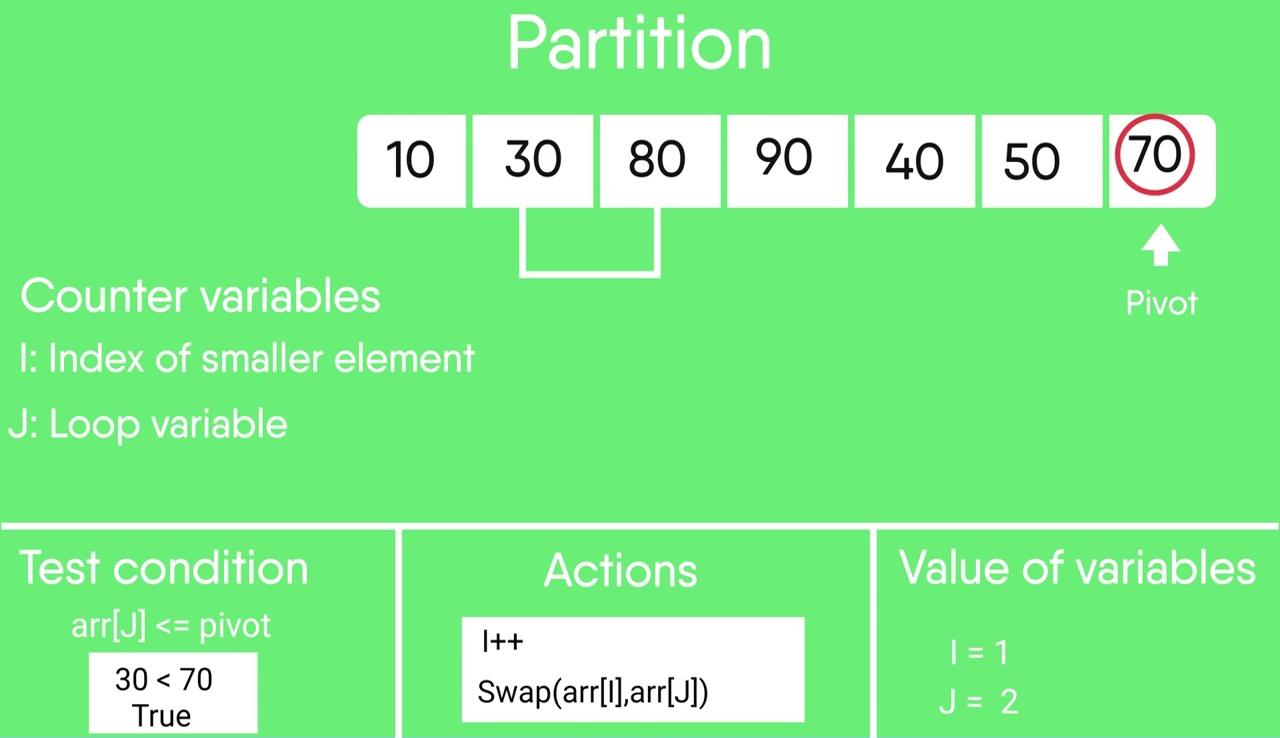
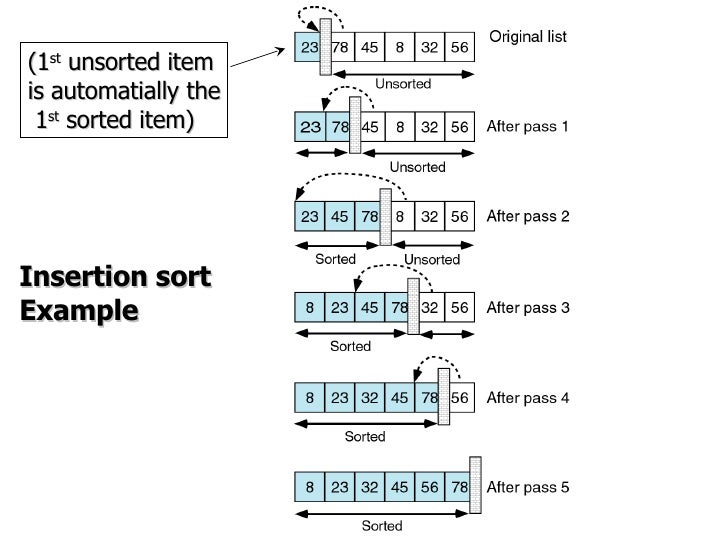
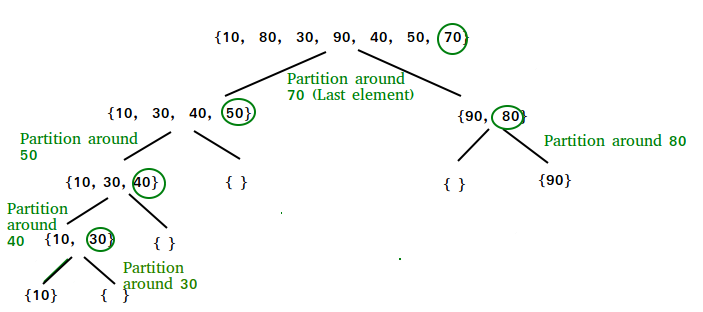
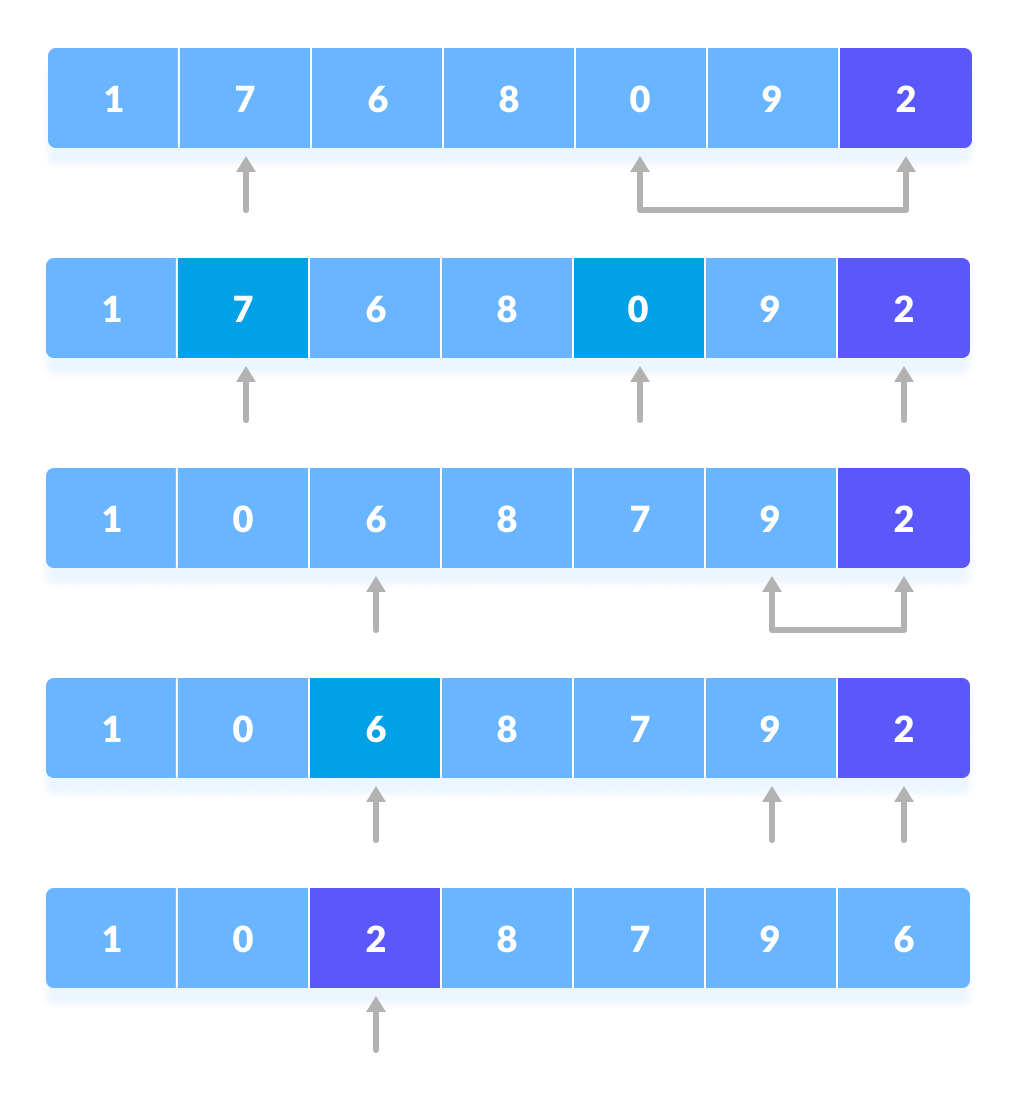
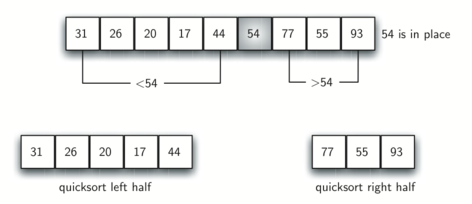
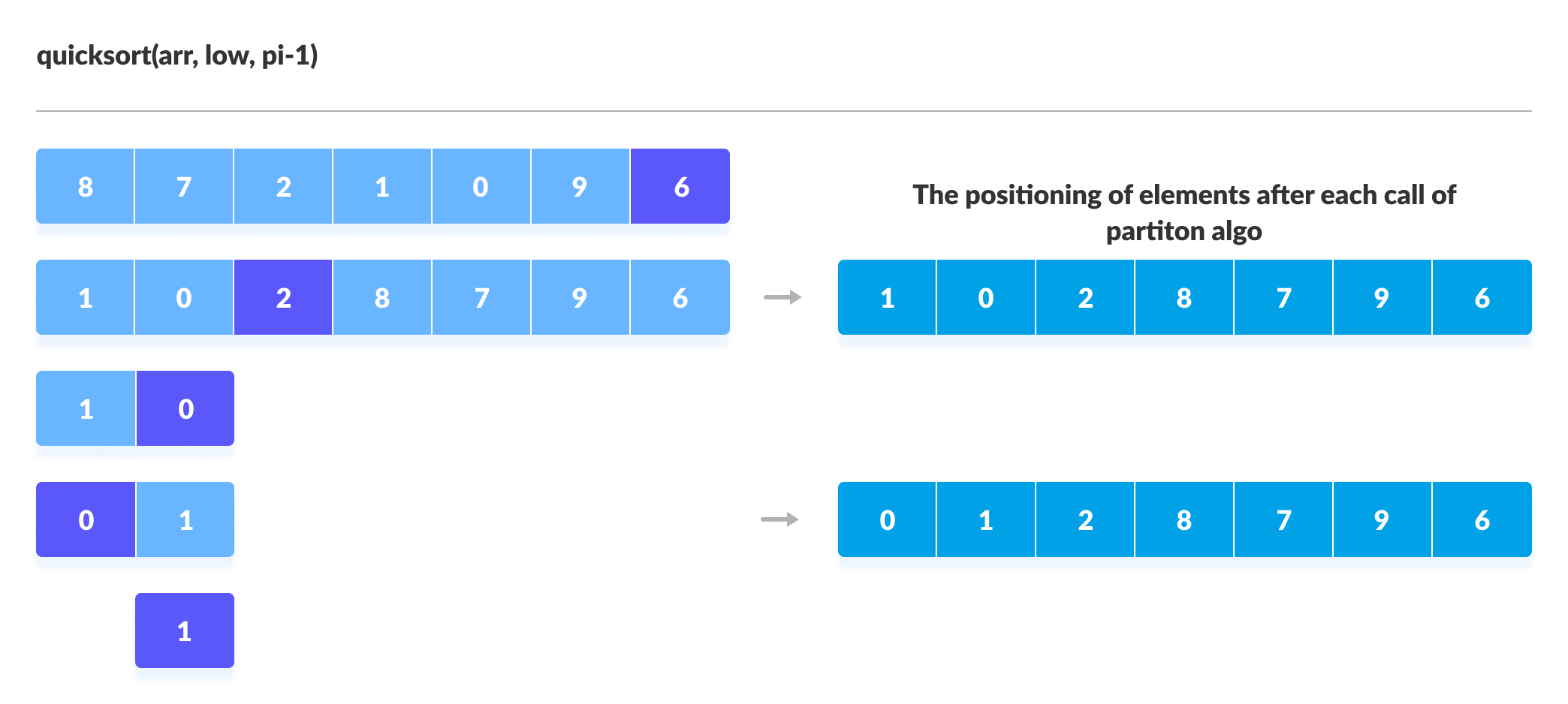
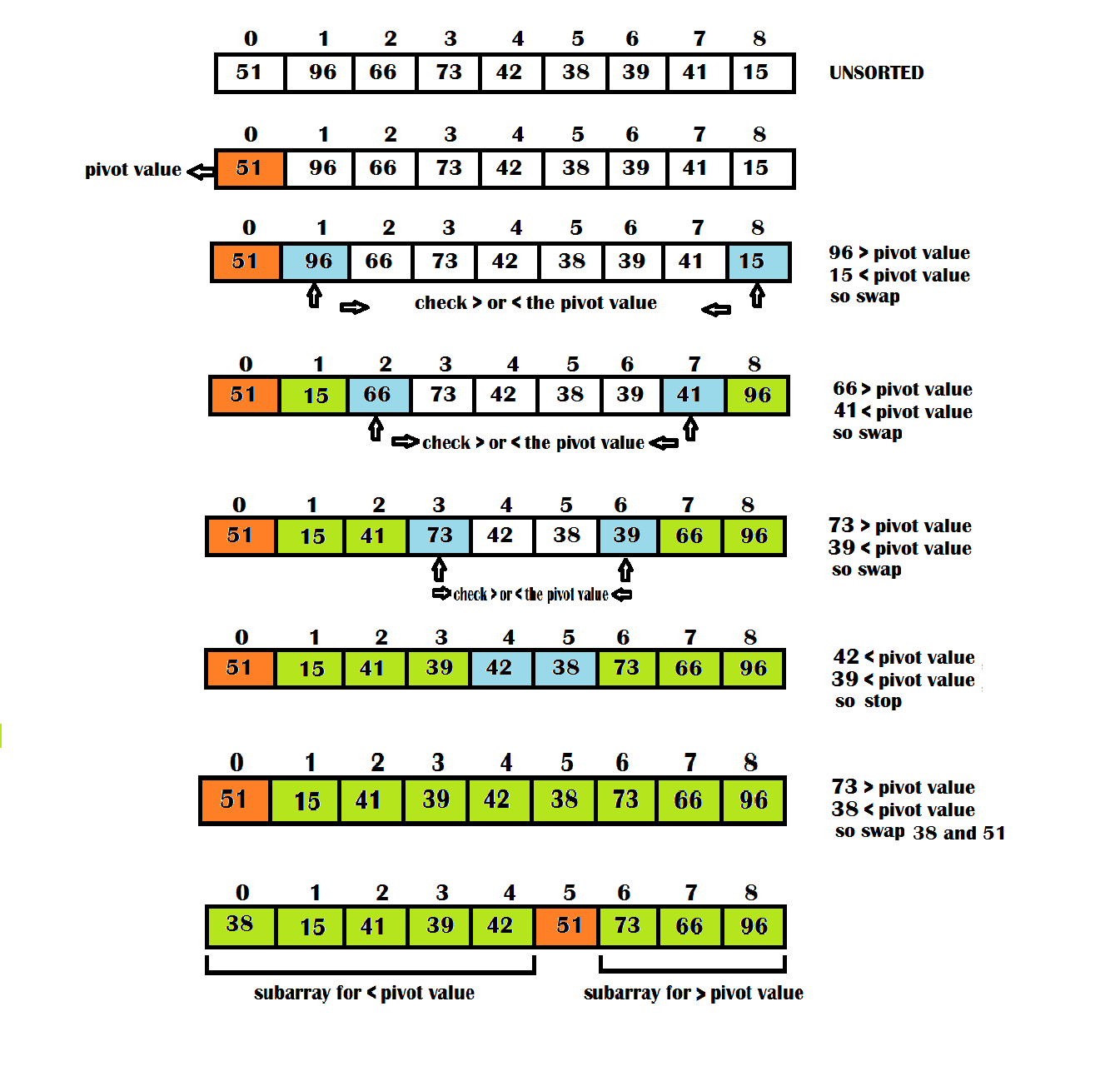
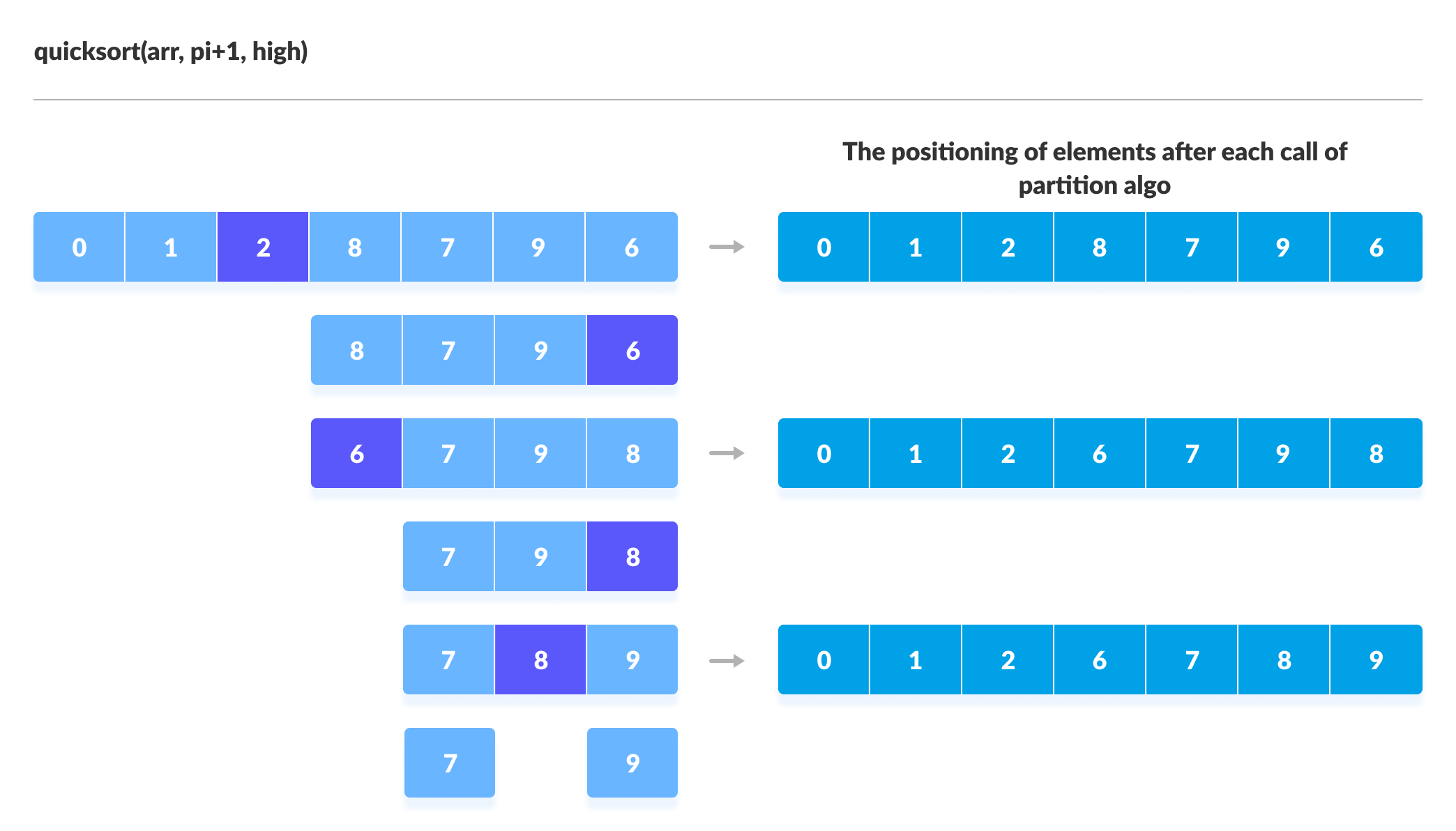
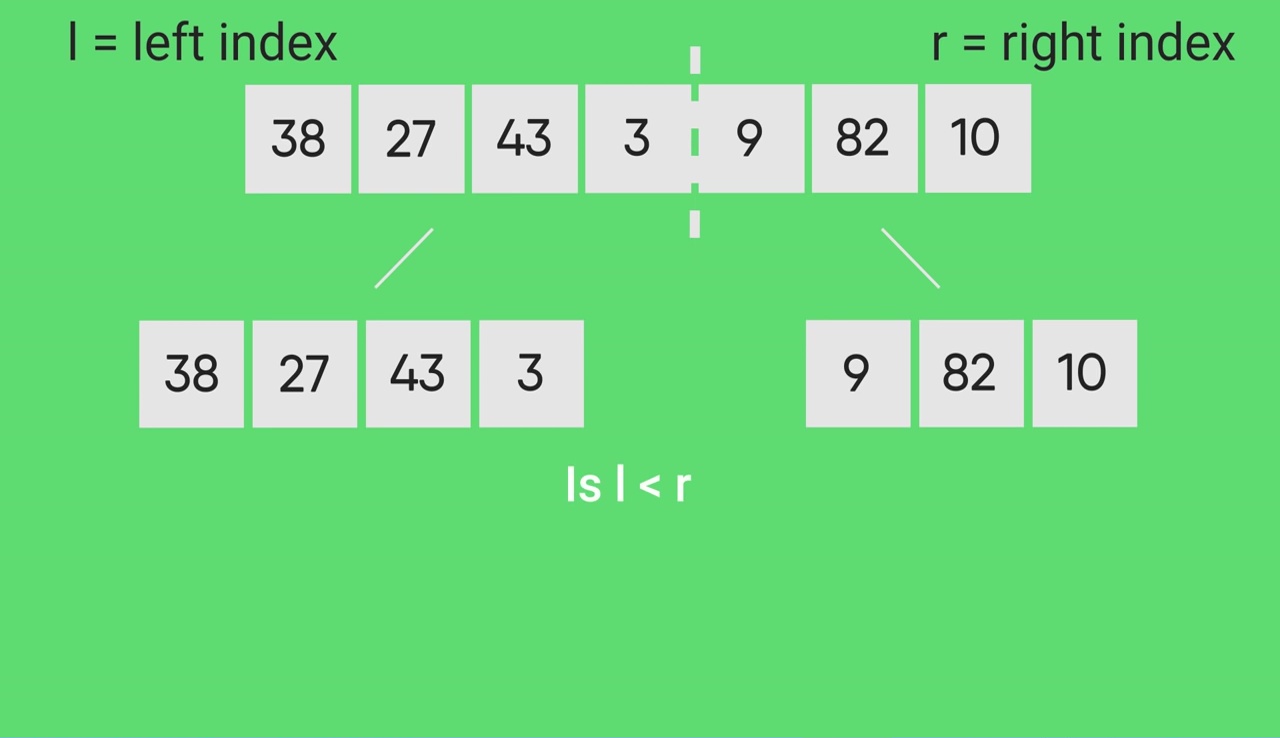
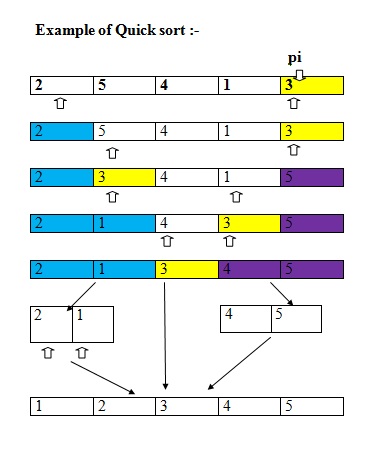
Quick sort c linked list. Take rightmost element as the pivot. In this problem on the sorting of a linked list the alternate sort means sorting in such a way that the 1st node contains data with the minimum value the 2nd node contains data with maximum value 3rd with the next minimum second minimum value and so on. Given a linked list we will sort the linked list using quick sort. In quick sort first we need to choose a value called pivot preferably the last element of the array.
Following is c implementation for same. The basic ideas of implementing quicksort in arrays and in lists are same also based on partition but there s one thing different. The important things about implementation are it changes pointers rather swapping data and time complexity is same as the implementation for doubly linked list. Then we arrange the smaller values towards the left side of the pivot and higher values towards the right side of the pivot.
The idea is simple we first find out pointer to last node. In partition we consider last element as pivot. Following is c implementation for the doubly linked list. Following is c implementation for same.
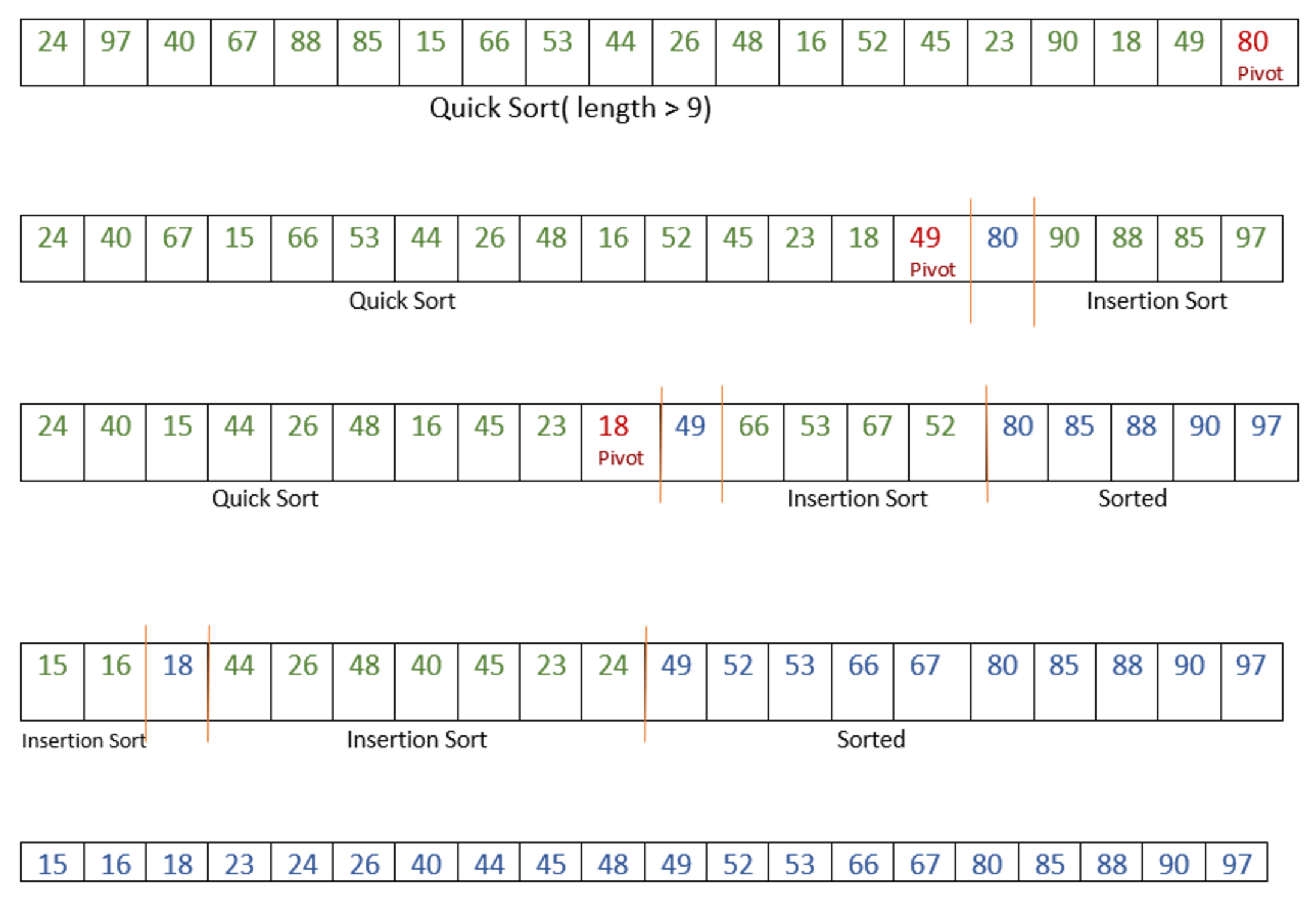
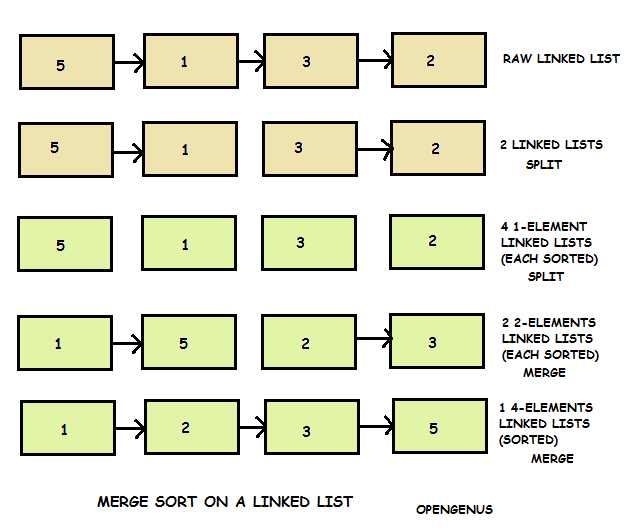
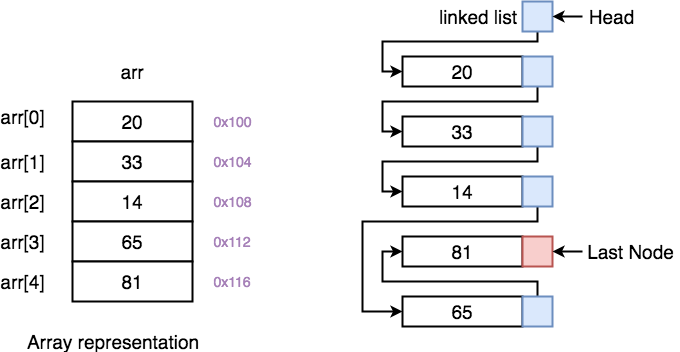
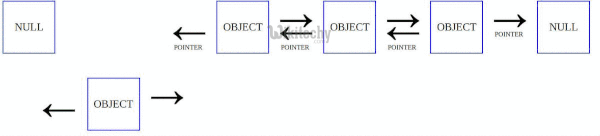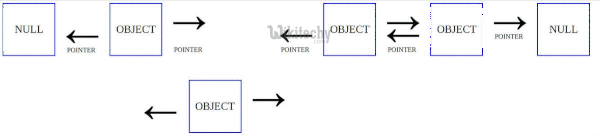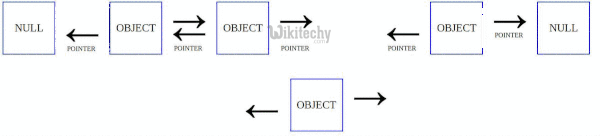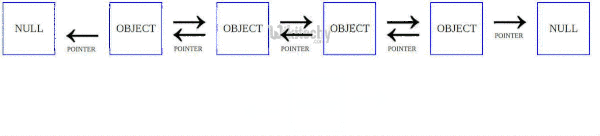
A linked list is a linear data structure that stores elements and also stores a pointer to the next data node. Recently while implement a list template i trying to migrate quick sort method to doubly linked list. These two operations are performed recursively until there is only one element left at both the side of the pivot. Quicksort algorithm is based on the concept of divide and conquer where we do all the main work of sorting while dividing the given data structure can be an array or in this case a linked list and during merging the data back absolutely no processing is done data is simply combined back together.
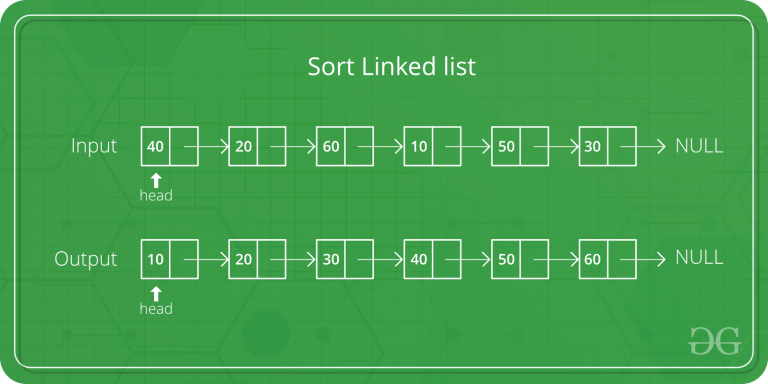
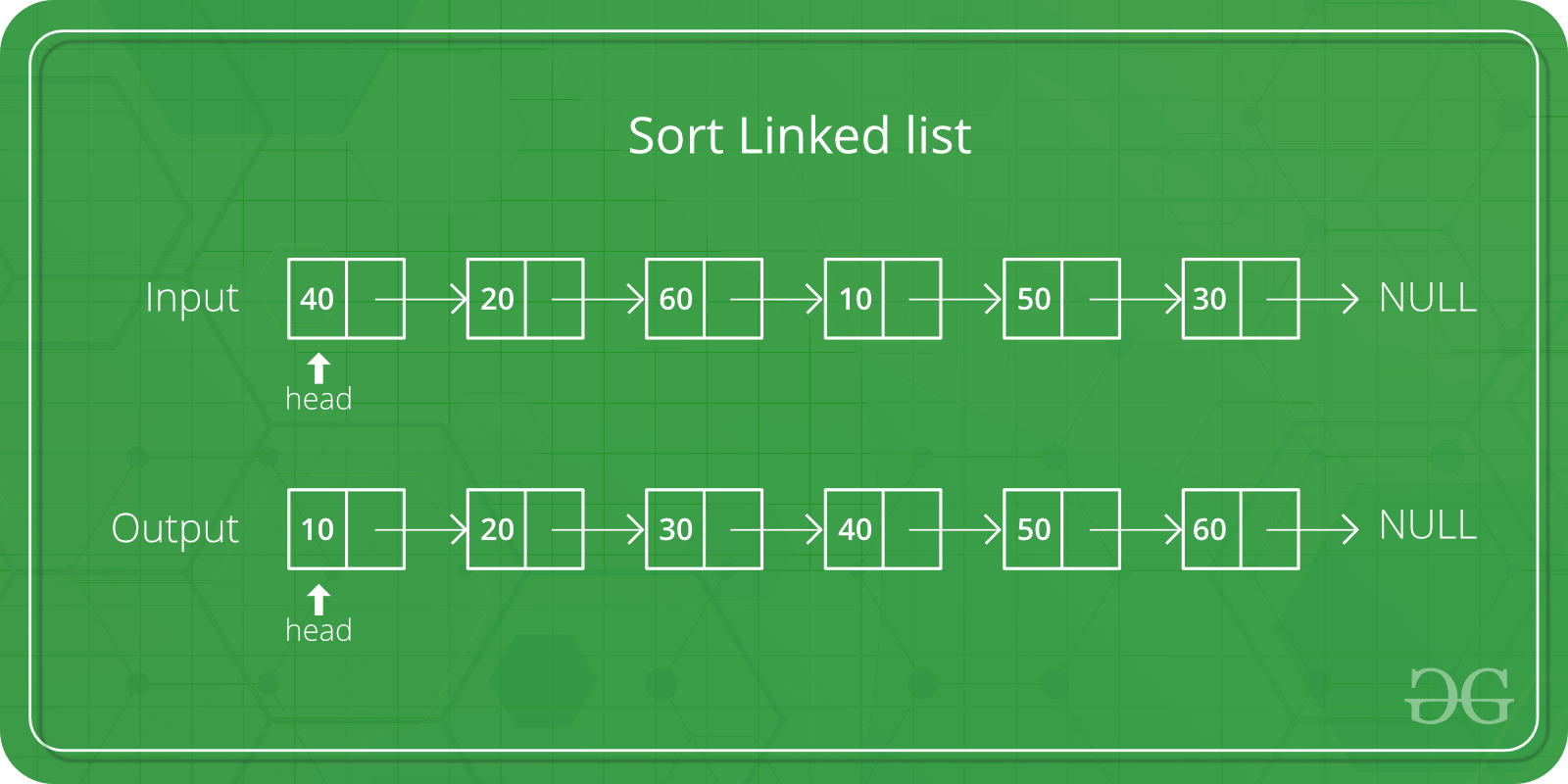
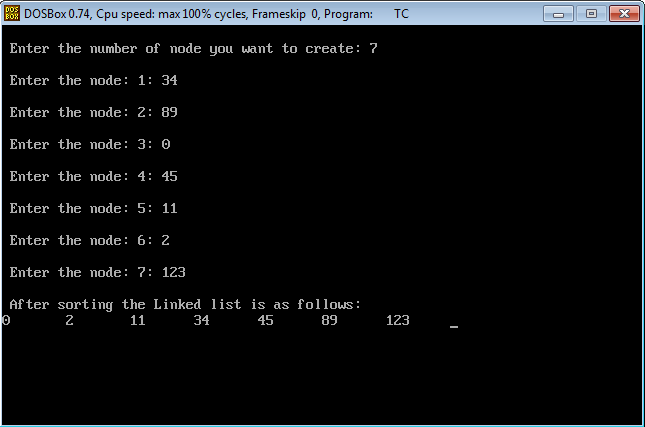
Linked list before sorting 23 1 50 15 16 6. Linked list after sorting 1 6 15 16 23 50. Following is c implementation for doubly linked list. The list does not support random access based on index.
The important things about implementation are it changes pointers rather swapping data and time complexity is same as the implementation for doubly linked list. Quicksort on singly linked list was given as an exercise. Once we have pointer to last node we can recursively sort the linked list using pointers to first and last nodes of linked list similar to the above recursive function where we pass indexes of first and last array elements. Once we have a pointer to the last node we can recursively sort the linked list using pointers to first and last nodes of a linked list similar to the above recursive function where we pass indexes of first and last array elements.
O in this method the main idea is to swap pointers rather than swaping data. The partition function for linked list is also similar to partition for arrays. The idea is simple we first find out pointer to the last node.